Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries have taken over the world. It is the most popular storage option. However it is a very polluting option. That’s why scientists are looking for less polluting options with renewable raw materials. Here we present five options.
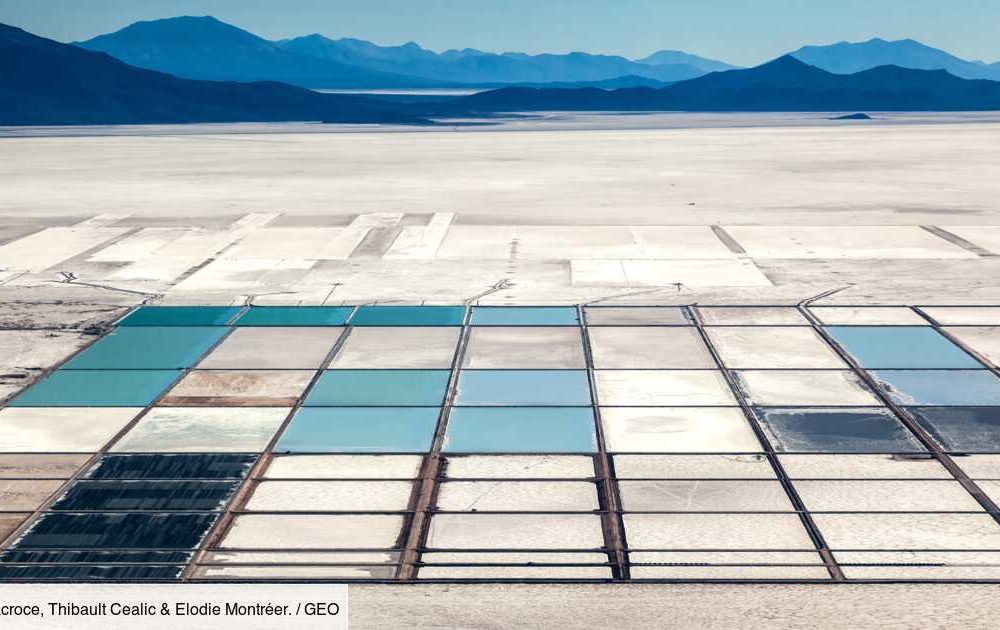
1 . Salt
The same environmental impact, which means that it could be a viable option to replace it. The solution could be sodium-ion batteries. Sodium-ion technology does not consume any scarce resources – its production does not require rare lithium salts – just table salt is sufficient. However, sodium is three times heavier than lithium, which means that sodium-ion batteries are also heavier. Sodium batteries can also be less powerful because of their lower battery voltage.
2 . Seawater
If salt batteries are one thing, why not use seawater? A team at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany has developed a prototype seawater battery. They have already attracted interest from South Korean investors, according to chief scientist Stefano Passerini. The world’s oceans contain about 180 billion tons of lithium. But because it’s diluted, researchers are designing numerous filters to try to selectively extract lithium from seawater to make the most of it.
3. Iron
Iron could be a powerful substitute for lithium. Last September, an article titled “Iron battery breakthrough could eat lithium’s lunch” appeared on Bloomberg. It focuses on a clean energy company in the U.S. state of Oregon that is buying a record amount of batteries that rely on “iron flow chemistry.” These could apparently store renewable energy longer and could “help overcome some of the reliability issues that have led to blackouts in California and record high energy prices in Europe.” The only limitation of iron-flow batteries is that they are much larger than lithium batteries. So the batteries won’t fit in a phone or car.
4. Silicon
Many scientists have touted silicon as a key ingredient that could change batteries. It will not replace lithium, but will be added to lithium batteries, meaning they will be cheaper and more efficient in the long run. Currently, lithium-ion batteries use graphite as a key ingredient. Graphite is made up of several layers of carbon stacked on top of each other. In conventional lithium-ion batteries, lithium ions slip through the gaps between these layers, causing losses. Replacing graphite with silicon could create lighter, safer batteries. “Silicon as an anode for lithium-ion batteries represents the ‘Holy Grail’ for researchers in this field,” said expert professor Apparao M. Rao, director of the Clemson Nanomaterials Institute in South Carolina, USA.
5. Magnesium
Magnesium is currently being studied as a potentially powerful ingredient in future batteries. It is an element that can carry a large +2 charge, more than lithium and sodium. Batteries made from magnesium metal can have higher energy density, higher stability and lower cost than today’s lithium-ion batteries, scientists found in a study. Magnesium has another advantage. Unlike lithium, each magnesium atom releases two electrons during the battery’s discharge phase. This allows almost twice as much power to be delivered.
Follow us on Social Media for more electric and hybrid car fresh news:
Instagram & facebook : @movo.eng
Twitter : @movo_fr
TikTok : @movo.fr
If you are interested in electric and hybrids car rental, please check our website and rent a luxury electric and hybrid car from our large selection.
To continue reading, do not hesitate to consult our article about la DeLorean DMC





Leave a Reply